
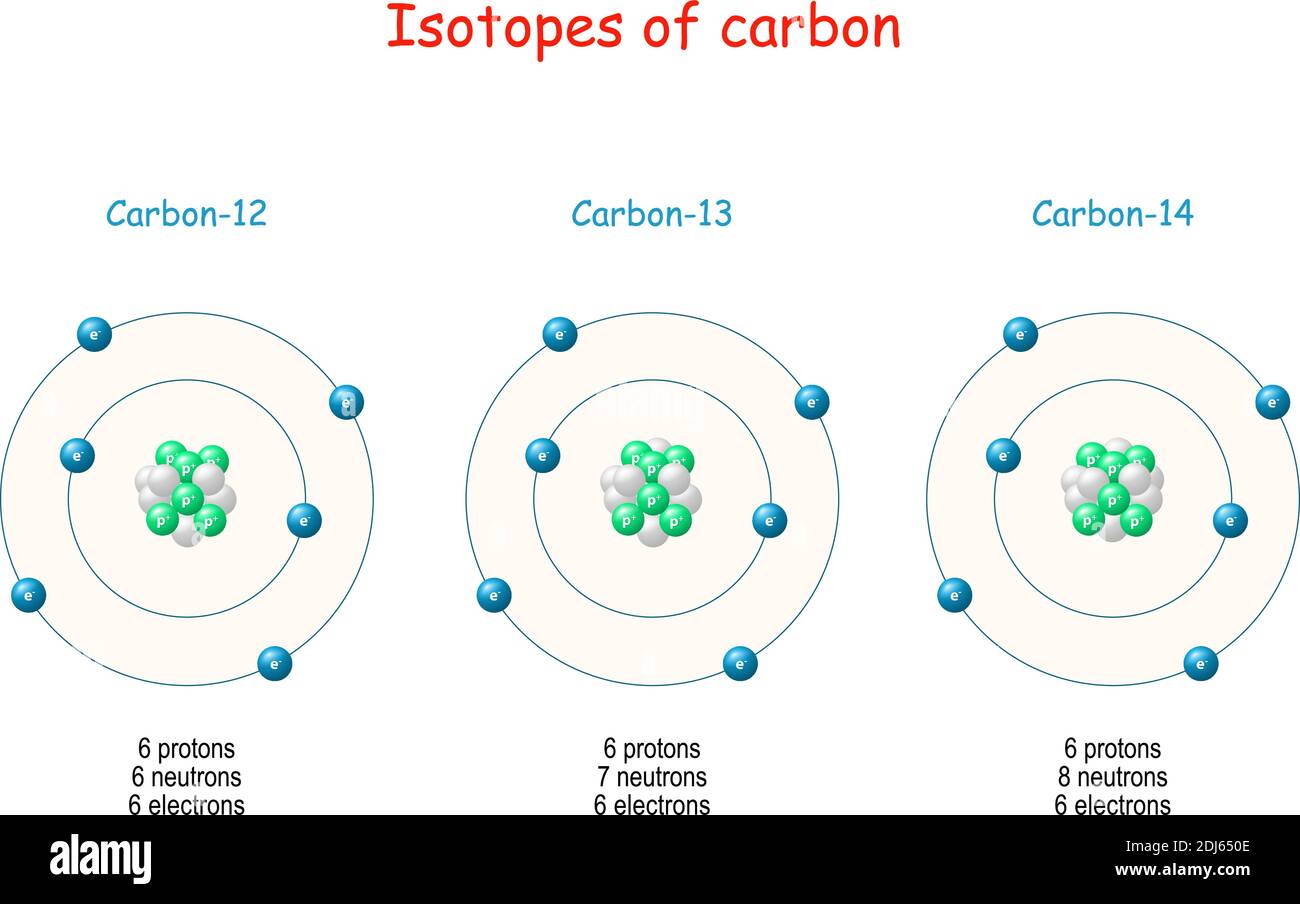
The subscript indicating the atomic number is actually redundant because the atomic symbol already uniquely specifies Z. The isotope of carbon that has 6 neutrons is therefore C 6 12. An isotope of any element can be uniquely represented as X Z A, where X is the atomic symbol of the element. In a typical sample of carbon-containing material, 98.89% of the carbon atoms also contain 6 neutrons, so each has a mass number of 12.
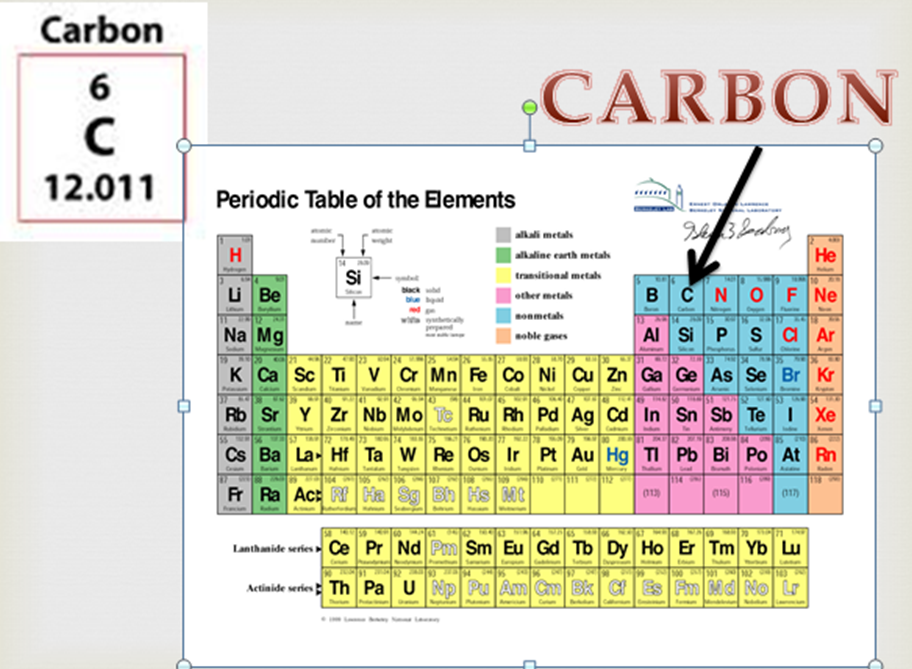
The element carbon (C) has an atomic number of 6, which means that all neutral carbon atoms contain 6 protons and 6 electrons. The isotopes of an element differ only in their atomic mass, which is given by the mass number ( A) The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of an element., the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons. All isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which means they exhibit the same chemistry. Atoms that have the same number of protons, and hence the same atomic number, but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes Atoms that have the same numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Unlike protons, the number of neutrons is not absolutely fixed for most elements. Recall from Section 1.5 "The Atom" that the nuclei of most atoms contain neutrons as well as protons. German for “wolf stone” because it interfered with the smelting of tin and was thought to devour the tin Table 1.4 Element Symbols Based on Names No Longer in Use Elementįrom Cyprium, Latin name for the island of Cyprus, the major source of copper ore in the Roman Empire As you work through this text, you will encounter the names and symbols of the elements repeatedly, and much as you become familiar with characters in a play or a film, their names and symbols will become familiar. Examples are in Table 1.4 "Element Symbols Based on Names No Longer in Use". Examples are Fe for iron, from the Latin ferrum Na for sodium, from the Latin natrium and W for tungsten, from the German wolfram. Some of the symbols used for elements that have been known since antiquity are derived from historical names that are no longer in use only the symbols remain to remind us of their origin. Elements have also been named for their properties, for the native country of the scientist(s) who discovered them, for eminent scientists, for gods and goddesses, and for other poetic or historical reasons. In most cases, the symbols for the elements are derived directly from each element’s name, such as C for carbon, U for uranium, Ca for calcium, and Po for polonium. The semimetals lie along a diagonal line separating the metals and nonmetals. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.įigure 1.24 The Periodic Table Showing the Elements in Order of Increasing ZĪs described in Section 1.7 "Introduction to the Periodic Table", the metals are on the bottom left in the periodic table, and the nonmetals are at the top right. The chemistry of each element is determined by its number of protons and electrons. The names of the elements are listed in the periodic table, along with their symbols, atomic numbers, and atomic masses. in which each element is assigned a unique one-, two-, or three-letter symbol. ( Figure 1.24 "The Periodic Table Showing the Elements in Order of Increasing " also see Chapter 32 "Appendix H: Periodic Table of Elements"), We will explain the rationale for the peculiar format of the periodic table in Chapter 7 "The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends". The known elements are arranged in order of increasing Z in the periodic table A chart of the chemical elements arranged in rows of increasing atomic number so that the elements in each column (group) have similar chemical properties. The atomic number is therefore different for each element. The identity of an element is defined by its atomic number ( Z) The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element., the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element.
Rutherford’s nuclear model of the atom helped explain why atoms of different elements exhibit different chemical behavior.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
